Carbs have always been a hot topic in health and nutrition. For some, they’re a comfort food—think pasta dinners or warm bread at the table. For others, they’re the enemy, blamed for weight gain or blood sugar spikes. The truth lies somewhere in between. Carbohydrates are neither saints nor villains; they are simply fuel. Understanding what carbohydrates are, how they work, and which ones to prioritize can transform the way you eat and feel.
This article will break down Carbohydrates in a simple, relatable way. By the end, you’ll know which carbs to embrace, which to limit, and how to make them work for your lifestyle.
What Are Carbs and Why Do They Matter?
Carbs, or carbohydrates, are one of the three main macronutrients, alongside protein and fat. They are the body’s preferred energy source. When you eat Carbohydrates, your body converts them into glucose, which fuels everything from your brain to your muscles.
Types of Carbohydrates
- Sugars: Simple carbs found in candy, soda, fruit, and some dairy.
- Starches: Complex carbs in foods like rice, bread, and potatoes.
- Fiber: A non-digestible carb that helps digestion and promotes gut health.
Why They Matter
Carbohydrates aren’t just about energy. Fiber-rich carbs can reduce cholesterol, improve digestion, and keep you full longer. On the other hand, refined carbs can cause blood sugar spikes, which is why the type of carb you choose is critical.
Table: Simple vs Complex Carbohydrates
| Type | Examples | Effect on Body | Nutritional Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Simple Carbs | Candy, soda, pastries | Quick energy, blood sugar spike | Low in nutrients |
| Complex Carbs | Whole grains, legumes, veg | Steady energy, stable glucose | High in fiber & vitamins |
Types of Carbohydrates – Simple vs Complex Carbs
Carbohydrates are not created equal. Knowing the difference can help you make better food choices.
Simple Carbs: Quick but Short-Lived Energy
These are sugars that the body digests quickly. You’ll find them in processed foods, sweets, and sugary drinks. They give you a quick energy boost but often leave you hungry soon after.
Complex Carbs: Long-Lasting Fuel
Complex carbs take longer to digest, providing sustained energy. Foods like oats, quinoa, lentils, and vegetables fall into this category. They also contain vitamins, minerals, and fiber, making them essential for long-term health.

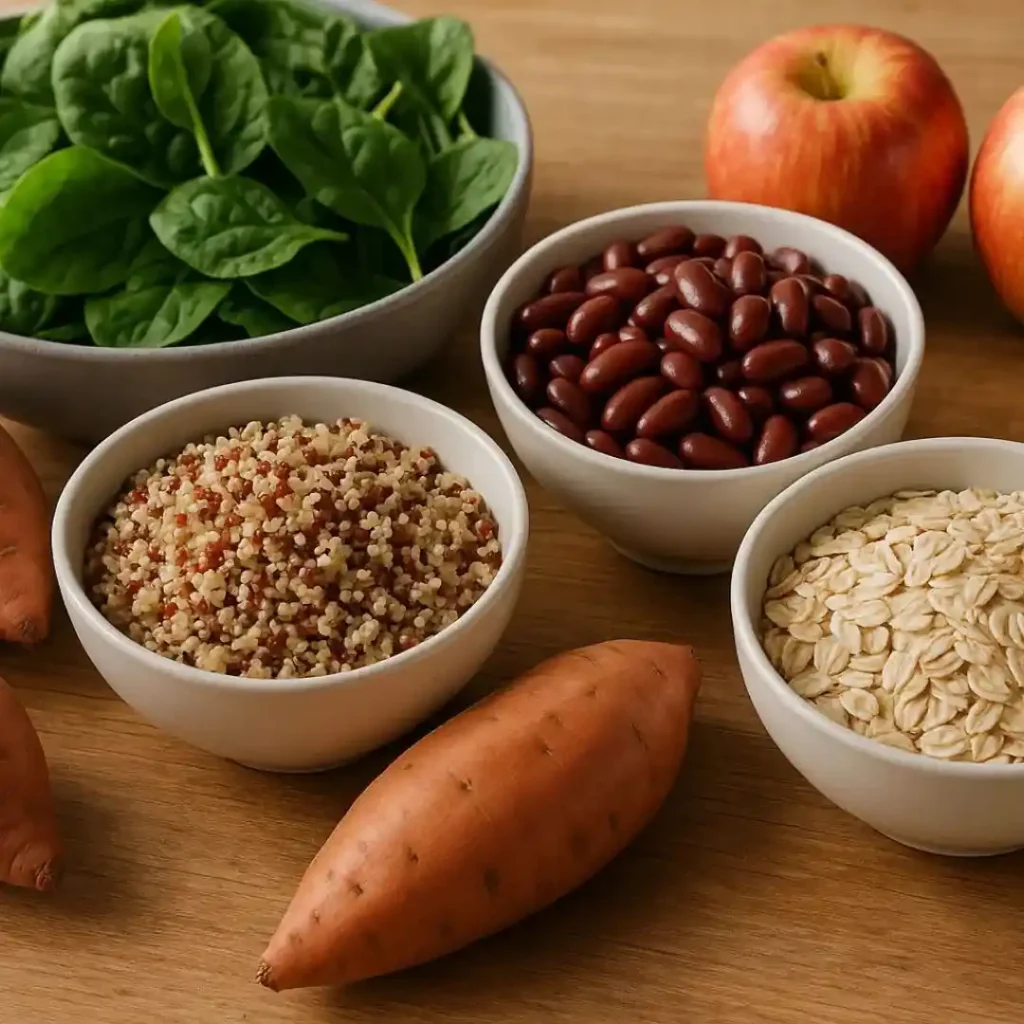
Healthy Carbohydrates to Include in Your Diet
- Whole grains like brown rice, oats, quinoa
- Fruits such as apples, berries, oranges
- Vegetables like sweet potatoes, broccoli, spinach
- Legumes including beans, lentils, chickpeas
Want to add more superfoods to your diet? Discover the Top Benefits of Pomegranate, a High-Fiber, Low-Sugar Fruit Packed with Antioxidants and see why it deserves a spot on your plate.
Carbohydrates and Your Health: Benefits and Risks
Health Benefits of Carbohydrates
- Provide steady energy for daily activities and workouts
- Support brain function, which relies primarily on glucose
- Fiber improves digestion and supports a healthy gut microbiome
Risks of Overeating Refined Carbs
Consuming too many refined Carbohydrates—like white bread, soda, or pastries—can lead to obesity, insulin resistance, and higher risks of type 2 diabetes.
Carbohydrates in Popular Diets
- Low-carb diets (Atkins, keto) limit Carbohydrates to promote fat burning.
- Mediterranean diet emphasizes whole carbohydrates such as whole grains, fruits, and legumes.
- Balanced diets recommend Carbohydrates as 45–65% of daily calories.
Starting your keto journey or looking for the perfect gift? Get the Keto Cheat Sheets Magnets Booklet—a handy keto food chart and meal guide designed for beginners and keto lovers. Make meal planning simple, fun, and effective with this must-have low-carb kitchen companion. Grab yours today on Amazon and stay on track with your goals!
How Many Carbs Should You Eat Per Day?
Recommended Intake
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the American Heart Association, Carbohydrates should make up 45–65% of daily calories. That means if you eat 2000 calories per day, 900–1300 should come from Carbohydrates (225–325 grams).
Carb Needs Based on Lifestyle
- Athletes: 5–7 grams per kilogram of body weight for training days.
- Sedentary adults: 3–4 grams per kilogram.
- Diabetics or weight-loss goals: 40–50% of calories from carbs, focusing on high-fiber sources.
Table: Daily Carb Needs
| Lifestyle | Carbs per Day (approx.) | Example Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Sedentary Adult | 150–200g | Vegetables, whole grains |
| Active Adult | 225–300g | Oats, fruits, rice, legumes |
| Athlete | 300–450g | Whole grains, pasta, potatoes |
Choosing the Right Carbs for a Healthy Lifestyle
Best Sources of Healthy Carbohydrates
- Quinoa, oats, brown rice
- Sweet potatoes, leafy greens
- Apples, bananas, berries
- Lentils, black beans, chickpeas

Satisfy your sweet tooth without the guilt! The Quest Nutrition Crispy Chocolate Caramel Pecan Hero Protein Bar packs 15g of protein, just 1g of sugar, and only 3g net carbs. Gluten-free and keto-friendly, it’s the perfect on-the-go snack to fuel your day. Order your 12-count box today and enjoy a delicious, healthier way to snack!
Foods to Limit or Avoid
- Sugary drinks and candy
- Refined grains (white bread, pasta)
- Processed snack foods like chips and cookies
Practical Tips for Smarter Carb Choices
- Replace white rice with quinoa or brown rice
- Choose whole wheat bread instead of white bread
- Snack on fruit instead of pastries
- Add legumes to soups and salads for extra fiber
FAQs About Carbohydrates
Which foods are carbs?
Carbohydrates are found in a wide variety of foods. Common carbohydrate sources include grains like rice, bread, pasta, and oats; starchy vegetables such as potatoes and corn; legumes like beans and lentils; fruits including apples, bananas, and berries; and dairy products like milk and yogurt. Even sugary snacks, sodas, and pastries are carb-rich, though these are less nutrient-dense options.
What are the carb foods to avoid?
It’s best to limit highly processed and refined carb foods. These include white bread, sugary cereals, candy, cakes, cookies, soda, and other sweetened beverages. These foods are low in fiber and nutrients but high in added sugars, which can spike blood sugar and lead to cravings, weight gain, and other health risks when eaten in excess.
What are healthy carbohydrates to eat?
Healthy Carbohydrates are nutrient-dense, fiber-rich, and minimally processed. Good examples include whole grains like quinoa, oats, and brown rice; legumes such as lentils, black beans, and chickpeas; fruits like apples, oranges, and berries; and vegetables including broccoli, carrots, and sweet potatoes. These carbs provide steady energy, vitamins, and minerals while supporting digestive health.
What do carbs do to a body?
Carbs are the body’s primary fuel source. Once eaten, they break down into glucose, which powers your brain, muscles, and vital organs. Fiber-rich Carbohydrates also aid digestion, regulate blood sugar, and keep you full longer. However, too many refined Carbohydrates can lead to energy crashes, weight gain, and an increased risk of health issues such as type 2 diabetes.
Final Thoughts – Making Peace With Carbohydrates
Carbs aren’t the enemy; they are essential fuel. The key is choosing the right kind—fiber-rich, minimally processed, nutrient-dense Carbohydrates. By focusing on balance and moderation, you can enjoy Carbohydrates without guilt while supporting your health and fitness goals.
Disclaimer: This content is for educational purposes only. It should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult a doctor or dietitian before making significant dietary changes.
This article may contain affiliate links. If you purchase through these links, we may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. We only recommend products we truly trust.